1 山东大学物理学院晶体材料国家重点实验室,山东 济南 250100
2 南开大学电子信息与光学工程学院微尺度光学信息基础科学重点实验室,天津 300350
3 山东师范大学物理与电子科学学院山东省光场调控工程技术中心,山东省光学与光子器件重点实验室,山东 济南 250358
利用飞秒激光直写技术制备Tm∶YAP光波导并实现1.9 μm波导调Q锁模激光输出。结合具有金属特性的NbSe2薄膜作为可饱和吸收元件进行光学调制,波导激光输出的激光脉冲重复频率为7.8 GHz,最短脉宽为62 ps。这也是已报道的从Tm∶YAP波导中获得的最短激光脉宽。通过调整泵浦光的偏振,可以获得1855.87/1892.54 nm的双波长激光输出。结果表明,具有金属特性的NbSe2薄膜在调制中红外超快脉冲激光器方面具有较大的应用价值。此外,双波长输出的紧凑型Tm∶YAP波导脉冲激光器在多功能集成光子学研究方面具有较好的应用前景。
激光器 飞秒激光直写 波导激光 Tm∶YAP NbSe2 光学学报
2023, 43(16): 1623018

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shandong Provincial Engineering and Technical Center of Light Manipulations and Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Optics and Photonic Device, School of Physics and Electronics, Shandong Normal University, Jinan 250358, China
2 Key Laboratory of Optical Information Science and Technology, Ministry of Education, Institute of Modern Optics, Nankai University, Tianjin 300071, China
3 School of Physical Science and Technology, Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, China
Depressed cladding waveguides are fabricated in Pr:LiYF4 (YLF) crystal by femtosecond laser inscription following a helical scheme. With the optimized parameters, the propagation loss of the waveguide is around 0.12 dB/cm for multimode guiding. Under optical pumping with InGaN laser diodes at 444 nm, efficient waveguide lasers in the orange around 604 nm (-polarized) are achieved with minimum lasing threshold of 119.8 mW, maximum slope efficiency of 16.6%, and maximum output power of 120.6 mW. Benefiting from their optimized performances, the waveguides produced in this work are promising for applications as compact orange laser sources.
femtosecond laser helical inscription Pr:YLF crystal optical waveguide laser Chinese Optics Letters
2022, 20(12): 122201

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Science, Shandong Jianzhu University, Jinan 250101, China
2 Shandong Key Laboratory of Optical Communication Science and Technology, School of Physical Science and Information Technology, Liaocheng University, Liaocheng 252059, China
3 Shandong Provincial Engineering and Technical Center of Light Manipulations & Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Optics and Photonic Device, School of Physics and Electronics, Shandong Normal University, Jinan 250014, China
4 School of Physics, Shandong University, Jinan 250100, China
Lithium niobate (, LN) channel and ridge waveguides have been successfully fabricated by He ion implantation, which has energy of 500 keV and fluence of and is combined with lithography and the precise diamond dicing technique. The refractive index profile of the annealed LN planar waveguide was reconstructed. The propagation loss of the channel waveguide with a width of 10 µm and that of the ridge waveguides with widths of 25 µm and 15 µm were investigated by the end-face coupling method. In our work, the factors that affect the waveguide properties of channel and ridge waveguides were revealed.
lithium niobate waveguides ion implantation ridge waveguide channel waveguide Chinese Optics Letters
2022, 20(7): 071301

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Tianjin Key Laboratory of Micro-scale Optical Information Science and Technology, Institute of Modern Optics, Nankai University, Tianjin 300350, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Crystal Materials, Shandong University, Jinan 250100, China
3 Shandong Provincial Engineering and Technical Center of Light Manipulations & Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Optics and Photonic Device, School of Physics and Electronics, Shandong Normal University, Jinan 250358, China
4 Tianjin Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Sensor and Sensing Network Technology, Tianjin 300350, China
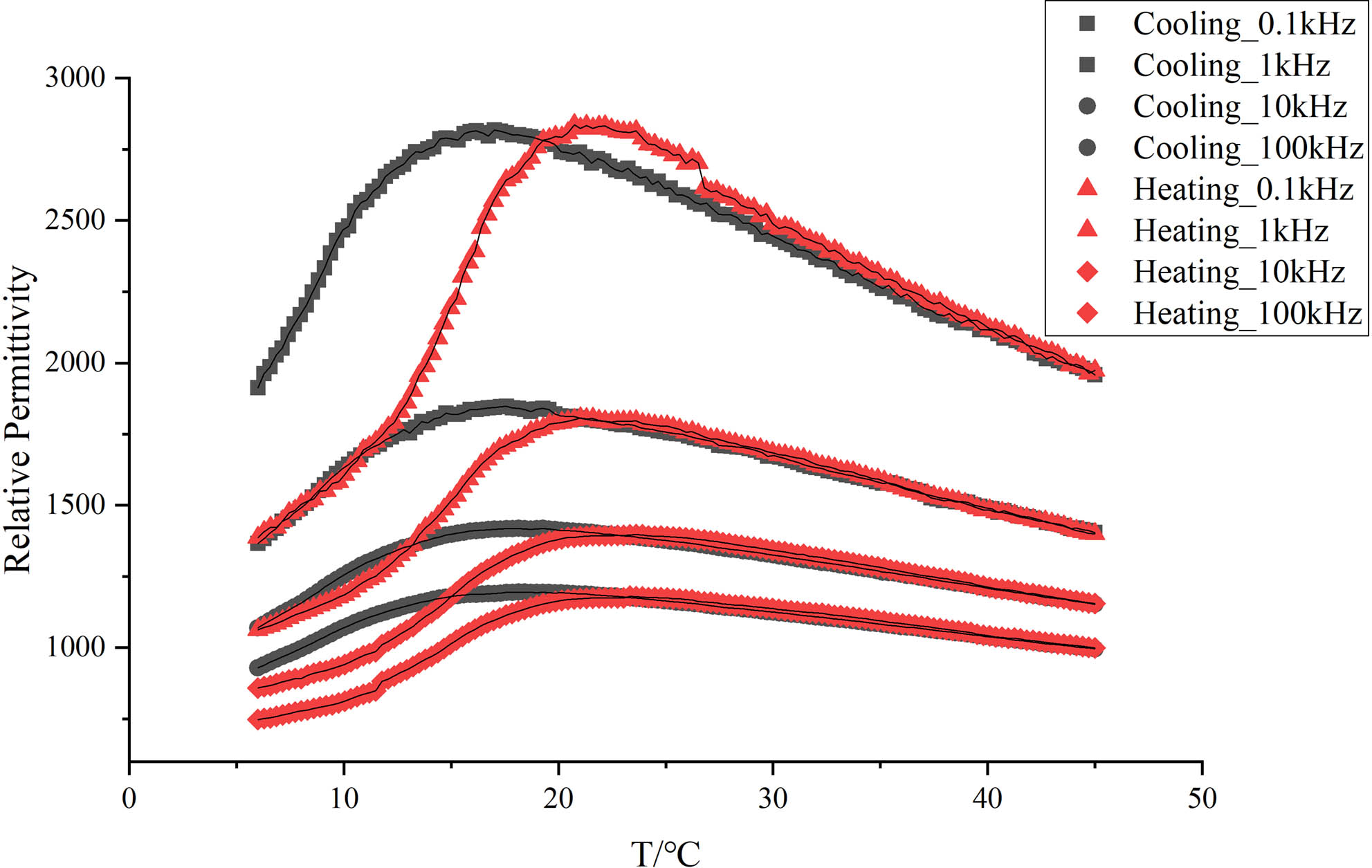
We report an interesting study of electric-field-induced transformation from a single domain ferroelectric state to the multiple domain ferroelectric state in a KTa1-xNbxO3 (KTN) crystal. Experimental results obtained using the confocal μ-Raman spectroscopy confirm the dynamic change of lattice structures induced by an external electric field. Furthermore, the dependence of relative permittivity on the applied voltage also indicates the transformation of ferroelectric states involving the processes of splintering, inversion, and re-formation of ferroelectric domains.
KTN ferroelectric state domain state transformation field-induced phenomenon Chinese Optics Letters
2021, 19(11): 111602

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physics, State Key Laboratory of Crystal Materials, Shandong University, Jinan 250100, China
2 Shandong Provincial Engineering and Technical Center of Light Manipulations & Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Optics and Photonic Device, School of Physics and Electronics, Shandong Normal University, Jinan 250014, China
Lithium niobate () is a versatile crystalline material for various photonic applications. With the recent advances in -on-insulator (LNOI) thin film technology, has been regarded as one of the most promising platforms for multi-functional integrated photonics. In this work, we present the field enhancement due to collective resonances in arrayed nanoantennas. These resonances arise from the enhanced radiative coupling of localized Mie resonances in the individual nanoparticles and Rayleigh anomalies due to in-plane diffraction orders of the lattice. We describe the pronounced differences in field enhancement and field distributions for electric and magnetic dipoles, offering valuable information for the design and optimization of high-quality-factor optical metasurfaces based on .
integrated optics nanophotonics lithium niobate Mie theory Chinese Optics Letters
2021, 19(6): 060013

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Science, Shandong Jianzhu University, Jinan 250101, China
2 Shandong Provincial Engineering and Technical Center of Light Manipulations & Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Optics and Photonic Device, School of Physics and Electronics, Shandong Normal University, Jinan 250014, China
3 School of Physics, Shandong University, Jinan 250100, China
We report on the fabrication and optimization of lithium niobate planar and ridge waveguides at the wavelength of 633 nm. To obtain a planar waveguide, oxygen ions with an energy of 3.0 MeV and a fluence of are implanted in the polished face of crystals. For planar waveguides, a loss of 0.5 dB/cm is obtained after annealing at 300°C for 30 min. The ridge waveguide is fabricated by the diamond blade dicing method on optimized planar waveguides. The guiding properties are investigated by prism coupling and end-face coupling methods.
lithium niobate waveguide precise dicing Chinese Optics Letters
2021, 19(6): 060009

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Center of Light Manipulations and Applications & Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Optics and Photonic Device, School of Physics and Electronics, Shandong Normal University, Jinan 250014, China
2 Institute of Modern Optics, Nankai University, Tianjin 300350, China
3 Institute of Photonics and Quantum Sciences, Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh EH14 4AS, UK
Optical channel waveguides with depressed cladding configurations have been produced in laser crystals by using ultrafast laser inscription. Waveguide properties are investigated in terms of guiding behaviors and localized laser-induced lattice damages. Under an optical pump of 808 nm light, continuous-wave waveguide lasing at 1.06 μm is achieved, with a single-mode operation and a minimum lasing threshold of 98.8 mW. Furthermore, the visible emissions of with short wavelengths ranging from 415 nm to 550 nm and long wavelengths from 550 nm to 625 nm are observed upon 808 nm laser excitation via the up-converted process. The intensity ratios of two wavelength ranges are proved to be tunable through changing the pumping polarizations.
femtosecond laser inscription optical waveguide CaF2 crystal laser upconversion Chinese Optics Letters
2021, 19(8): 081301
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Tianjin Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Sensor and Sensing Network Technology, Institute of Modern Optics, Nankai University, Tianjin 300071, China
2 Hubei Key Laboratory of Low Dimensional Optoelectronic Materials and Devices, Hubei University of Arts and Science, Xiangyang 441053, China
3 Advanced Materials Institute, Qilu University of Technology (Shandong Academy of Sciences), Jinan 250014, China
4 Shandong Provincial Engineering and Technical Center of Light Manipulations & Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Optics and Photonic Device, School of Physics and Electronics, Shandong Normal University, Jinan 250358, China
In this Letter, we report the existence and relaxation properties of a critical phenomenon on called a 3D super crystal that emerges at T = TC ? 3.5°C, that is, in the proximity of the Curie temperature of a Cu:KTN sample. The dynamics processes of a 3D super crystal manifest in its formation containing polarized nanometric regions and/or polarized clusters. However, with strong coupling and interaction of microcomponents, the characteristic relaxation time measured by dynamic light scattering demonstrates a fully new relaxation mechanism with a much longer relaxation time. As the relaxation mechanism of a relaxator is so-far undetermined, this research provides a novel perspective. These results can help structure a fundamental theory of ferroelectric relaxation.
KTN relaxation time dynamic light scattering micronano structure Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(2): 021901
1 山东师范大学物理与电子科学学院光场调控及应用中心, 山东省光学与光子器件技术重点实验室, 山东 济南 250014
2 萨拉曼卡大学应用物理系激光微加工组, 西班牙 萨拉曼卡 37008
采用飞秒激光对氟化钙晶体表面进行加工。通过调控激光参数,采用静止聚焦和动态扫描两种方式在晶体表面加工出一系列微结构(烧蚀孔和烧蚀线)。分别对两种加工方式烧蚀后的氟化钙晶体表面微结构进行系统研究,包括参数依赖关系、材料表面烧蚀阈值等。计算结果表明:在静止聚焦情况下,累积因子为0.0033;在动态扫描情况下,当扫描方向与激光偏振方向垂直或平行时,累积因子分别为0.0043和0.0052。飞秒激光加工过程中的脉冲累积效应能够对晶体的烧蚀产生重要影响。
物理光学 飞秒激光烧蚀 微结构 累积效应 氟化钙晶体
1 厦门大学信息科学与技术学院电子工程系, 福建 厦门 361005
2 厦门大学水声通信与海洋信息技术教育部重点实验室, 福建 厦门 361005
短脉冲宽度、高峰值功率的被动调Q固体激光器在医疗、光通信、激光点火和非线性光学转换等领域具有重大的应用价值。通过热键合技术和陶瓷烧结技术将激光增益介质与可饱和吸收体键合到一起形成的被动调Q复合激光材料,不仅能降低分离式激光增益介质和可饱和吸收体界面的散射和反射损耗,以降低激光腔内损耗,而且能消除二者之间的空气间隙,避免激光器在高峰值功率运行时产生的等离子体所造成的空气击穿导致激光晶体的损伤,保证激光器的稳定运行。针对基于复合材料的激光二极管抽运的小型化、集成化及高峰值功率的被动调Q固体激光器的研制和应用潜力,系统介绍了基于Nd:YAG-Cr4+:YAG、Yb:YAG-Cr4+:YAG复合材料的被动调Q固体激光器的研究进展及其发展趋势。
激光器 被动调Q 复合材料





